Oxygen storage capacity and thermal stability of the CuMnO2–CeO2 composite system†
Abstract
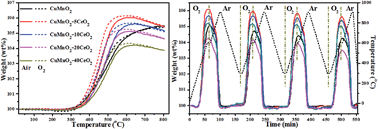
Fast and reversible oxygen diffusion in solid oxides depending on oxygen partial pressure at low temperatures is a promising strategy for improving the overall performance and service lifetime of many energy-related materials. However, the high energy required for the redox reaction of cations and their high thermodynamic barriers have impeded the realization of fast oxygen diffusion at low temperatures. Herein, we report enhanced oxygen diffusion and storage capacity of monoclinic crednerite CuMnO2 at a lower temperature by surface modification with CeO2. The fast and reversible oxygen uptake/release can be attributed to CeO2 that serves as a fast oxygen diffusion channel between bulk CuMnO2 and the surrounding atmospheres. Importantly, the amount of CeO2 in the CuMnO2–CeO2 composite system has a great effect on the total oxygen storage capacity and redox behaviour. Our findings could provide useful information for developing effective oxygen storage materials for wide energy-related applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Highlighting materials research in the UK for energy and sustainability

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...