Adsorption of CO2 on a micro-/mesoporous polyimine modified with tris(2-aminoethyl)amine†
Abstract
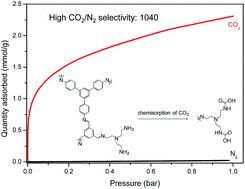
Amine-modified sorbents are relevant to the capturing of dilute carbon dioxide from gas mixtures, and micro-/mesoporous polymers are promising substrates due to their rich chemistry. Here, we prepared an aldehyde-rich polyimine with micro- and mesopores by a Schiff-base condensation of 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene and 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxaldehyde using an excess of aldehyde. The micropores were crucial to the physisorption of CO2, while the mesopores provided space for the post-modification with tris(2-aminoethyl)amine (tren) that induced the chemisorption of CO2. The amine modified polymer showed a high uptake of CO2 at low pressures (1.13 mmol g−1 at 0.05 bar and 273 K) and a high estimated CO2-over-N2 selectivity (1.04 × 103 at 273 K for 5 v%/95 v% CO2/N2 mixture). CO2 both physisorbed and chemisorbed on the amine-modified polyimine, which we confirmed by studying the CO2-amine chemistry using in situ FTIR spectroscopy and solid state 13C NMR spectroscopy. Carbamic acid formed during the chemisorption of CO2, as the CO2 reacted with the amine groups. Due to the formation of carbamic acid, the isosteric heat of adsorption was high, with values up to 80 kJ mol−1 at a low coverage of CO2. It appears that amine-modified porous polymers could be relevant to the removal of CO2 from gas streams with low concentrations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...