Role of Cr3+/Cr6+ redox in chromium-substituted Li2MnO3·LiNi1/2Mn1/2O2 layered composite cathodes: electrochemistry and voltage fade
Abstract
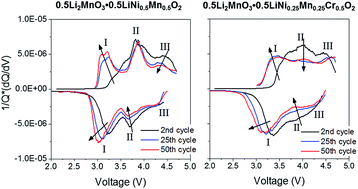
The effect of redox-active Cr substitution on the electrochemistry and voltage fade of a lithium-rich “layered–layered” composite cathode material has been investigated. A series of Cr-substituted 0.5Li2MnO3·0.5LiNi1/2Mn1/2O2 powder samples (i.e., Li1.2Ni0.2−2/xMn0.6−2/xCrxO2, where x = 0, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2) was synthesized via the sol–gel method. X-ray diffraction data confirmed the incorporation of Cr ions into the lattice structure. While similar initial charge capacities (∼300 mA h g−1) were obtained for all of the cathode samples, the capacity contribution from the Li2MnO3 activation plateau (at 4.5 V vs. Li) decreased with increasing Cr content. This finding suggests suppressed oxygen loss that triggers cation migration and voltage fade in subsequent cycles. Continued investigation revealed that the Cr substitution mitigates the voltage fade on charge but not discharge. The resulting insignificant effect of Cr substitution on mitigating voltage fade, in spite of decreased Li2MnO3 activation, is attributed to the additional instability caused by Cr6+ migration to a tetrahedral site, as evidenced by ex situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Our results provide the framework for a future redox active cation substitution strategy by highlighting the importance of the structural stability of the substituent itself.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...