Dielectric elastomer actuator with excellent electromechanical performance using slide-ring materials/barium titanate composites†
Abstract
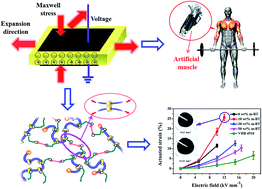
Dielectric elastomers are referred to as artificial muscles because of their excellent properties. However, the need for high operating voltage limits their practical application. A reduction of the operating voltage can be achieved with novel elastomers offering intrinsically high electromechanical sensitivity. In this work, slide-ring materials with a necklace-like molecular structure are prepared as dielectric elastomer materials. These slide-ring materials are found to exhibit high dielectric constants, low elastic moduli, and high electromechanical sensitivity due to their special structural characteristics. Barium titanate particles modified by γ-methacryloxypropyl trimethoxy silane (KH570) are incorporated into the slide-ring materials to further improve the actuated performance of the slide-ring materials. A high actuated strain (26%) at a relatively low electric field (12 kV mm−1) is obtained on the circular membrane actuator without any pre-strains, much more excellent than those of other dielectric elastomers reported in the literature. In addition, an obviously larger displacement is achieved by the slide-ring composite than that of commercial dielectric elastomer VHB 4910 on a cone-type actuator at the same electric field. These results demonstrate that our research might help to establish a new synthetic route to high performance dielectric elastomers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...