Adhesive hydrophobicity of Cu2O nano-columnar arrays induced by nitrogen ion irradiation
Abstract
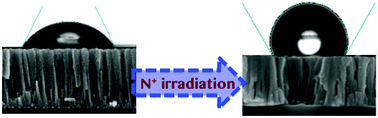
Low energy nitrogen ions are used in this work to manipulate wetting properties of the surface of the array of Cu2O nano-columns, which yields remarkable results. The nano-columnar thin films were grown on a highly conductive silicon surface by a sputter deposition technique. The films were irradiated at two different fluences of 5 × 1015 and 1 × 1016 ions per cm2, respectively. With increasing fluence the shape of column tip changes, columns are bent and porous channels between columns are clogged up. While the surface of the pristine sample is hydrophilic, the irradiated surface turns into hydrophobic but having adhesion properties. We have analysed the structural and chemical properties of the surface in detail to understand the initial and modified wetting properties. Furthermore, the temporal evolutions of different droplet parameters are investigated to realize the interactions between the water droplet, the sample surface and the atmosphere. We envisage that such modified surfaces can be beneficial for transport of a small volume of liquids with minimum loss and spectroscopic studies, where a small amount of water droplet is available for measurements.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...