Controlled self-assembly of a pyrene-based bolaamphiphile by acetate ions: from nanodisks to nanofibers by fluorescence enhancement†
Abstract
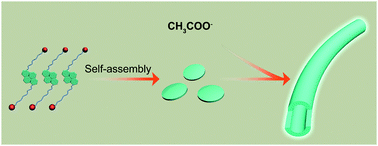
In this paper, a pyrene moiety is incorporated into a bolaamphiphile to form a novel molecule denoted PRB. Above the critical micelle concentration, PRB forms nanodisks in the aqueous solution. The addition of acetate ions induces a morphological change in self-assembled aggregates, which convert into nanofibers with a diameter of several nanometers. More interestingly, along with the morphological change, the fluorescence of the assemblies was enhanced concomitantly, which can be attributed to the binding effect of acetate ions on pyridinium head groups of PRB.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...