Multi-stimuli-responsive chiral organogels based on peptide derivatives†
Abstract
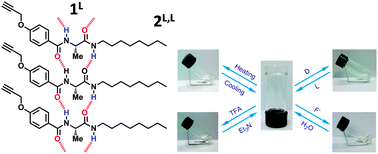
A series of chiral aryl amide compounds bearing peptide pendants have been investigated as low molecular weight gelators. A mechanistic study reveals that complementary hydrogen bonding from peptide pendants is the main driving force for the formation of organogels. This new class of organogels can exhibit multi-stimuli-responsive behavior upon applying (1) thermal, (2) pH, (3) enantiomeric purity, and (4) fluoride anion stimuli. Enantiomeric purity as a new external stimulus displays sensitive stimuli-responsiveness; only 0.02 equiv. of the enantiomer can completely disassemble the gel aggregate. They will serve as excellent smart materials with potential applications in chiral sensors, recognition, and separation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...