The fungal cerato-platanin protein EPL1 forms highly ordered layers at hydrophobic/hydrophilic interfaces
Abstract
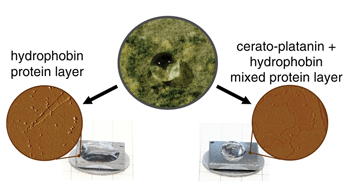
Cerato-platanin proteins (CPPs) and hydrophobins are two classes of small, secreted proteins that are exclusively found in fungi. CPPs are known as chitin-binding proteins, and were recently also shown to form protein layers at air/water interfaces, but the features of these layers were not investigated on the molecular level yet. In this study, by means of atomic force microscopy (AFM), EPL1, a member of the CPP family was shown to form highly ordered monolayers at a hydrophobic surface/liquid-interface. Furthermore, two new hydrophobins were analysed, and the influence of EPL1 on hydrophobin layers was studied in situ. Hydrophobins are amphiphilic proteins that are able to self-assemble at hydrophobic/hydrophilic interfaces, thereby inverting the polarity of the surface. This renders fungal growth structures such as spores water repellent. The combination of AFM data and wettability experiments led to the conclusion that in presence of both, hydrophobins and EPL1, a previously unknown hybrid layer is formed. This mixed protein layer is on one hand not inverting but enhancing the hydrophobicity of HOPG (highly oriented pyrolytic graphite), typical for EPL1, and on the other hand, it is stable and water insoluble, which is reminiscent of hydrophobin layers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...