Boronic acid–DMAPO cooperative catalysis for dehydrative condensation between carboxylic acids and amines†
Abstract
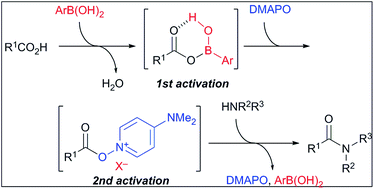
Arylboronic acid and 4-(N,N-dimethylamino)pyridine N-oxide (DMAPO) cooperatively catalyse the dehydrative condensation reaction between carboxylic acids and amines to give the corresponding amides under azeotropic reflux conditions. This cooperative use is much more effective than their individual use as catalysts, and chemoselectively promotes the amide condensation of (poly)conjugated carboxylic acids. The present method is practical and scalable, and has been applied to the synthesis of sitagliptin and a drug candidate.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Top 50 Articles of 2016: Energy and Catalysis

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...