A polyion complex sensor array for markerless and noninvasive identification of differentiated mesenchymal stem cells from human adipose tissue†
Abstract
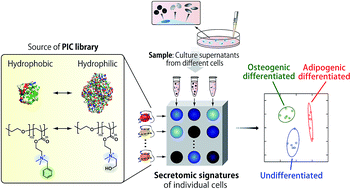
Currently available methods for stem cell evaluation require both prior knowledge of specific markers and invasive cell lysis or staining, hampering the development of stem cell products with assured safety and quality. Here, we present a strategy using optical cross-reactive sensor arrays for markerless and noninvasive identification of differentiated stem cell lineages with common laboratory equipment. The sensor array consists of a library of polyion complexes (PICs) between anionic enzymes and synthetic poly(ethylene glycol)-modified polyamines, which can recognize “secretomic signatures” in cell culture supernatants. Due to the reversible nature of PIC formation, the incubation of diluted culture supernatants with PICs caused enzyme release through competitive interactions between the secreted molecules and the PICs, generating unique patterns of recovery in enzyme activity for individual cell types or lineages. Linear discriminant analysis of the patterns allowed not only normal/cancer cell discrimination but also lineage identification of osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells, therefore providing an effective way to characterize cultured cells in the fields of regenerative medicine, tissue engineering and cell biology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...