Abstract
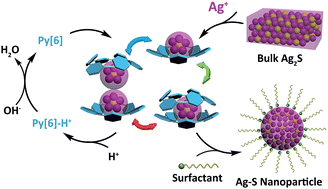
We report herein a new nanoparticlization process for the bulk-to-nano transformation of Ag2S by incorporating both top-down and bottom-up approaches. Bulk Ag2S was dissolved in solution with the assistance of a macrocyclic ligand, hexamethylazacalix[6]pyridine (Py[6]), to produce polynuclear silver sulfide cluster aggregates. All Ag–S cluster aggregates obtained in three crystalline complexes were protected by Py[6] macrocycles. Removing the protective Py[6] macrocycles by protonation led to the generation of unconventional Ag–S nanoparticles with a large energy gap. Theoretical calculations by a hybrid DFT method demonstrated that the silver sulfide clusters with high Ag/S ratio exhibited more localized HOMO–LUMO orbitals, which consequently enlarged their band gap energies. These experimental and theoretical studies broaden our understanding of the fabrication of nanomaterials by virtue of the advantages of both bottom-up and top-down methods and meanwhile provide a viable means of adjusting the band gap of binary nanomaterials independent of their size.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...