Functional holey graphene oxide: a new electrochemically transformed substrate material for dopamine sensing†
Abstract
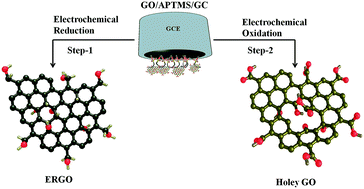
Increasing active sites through generating holes within the basal plane of graphene sheets is an effective strategy to enhance catalytic performance in various applications such as sensors, electrocatalysis, and electronics. In this study, we report a simple two-step electrochemical approach to convert graphene oxide (GO) into holey graphene oxide (HGO)—graphene sheets with holes ranging from several to tens of nanometers in diameter. The resultant HGO graphene has an order of magnitude more effective surface area than GO, and behaves almost as a reversible electrode system in terms of peak-to-peak seperation value (ΔE) and heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant (k0) towards the Fe(CN)63−/4− redox probe. Characterization of the HGO surface using atomic force microscopy (AFM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, and cyclic voltammetry confirmed generation of holes on the graphene sheets. β-Cyclodextrin (β-CD) was immobilized on ‘as prepared’ HGO demonstrating an additional advantage from the presence of oxygen-containing functional groups on the resultant HGO surface. The β-CD-HGO nanocomposite was investigated as a potential dopamine (DA) sensor material using amperometric techniques. The linear range for DA detection was 0.1–800 μM (N = 3), sensitivity was 4.4 nA μM−1 cm−2, and the detection limit was 7.6 nM (S/N = 3). In addition to enhanced catalytic performance, HGO can be easily modified with materials such as β-cyclodextrin, as well as nanoparticles, bioactive molecules, and stimuli responsive polymers, providing a promising sensor platform.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...