Structure-activity investigations on amphiphilic cationic copolymers of vinyl N,N-dimethylethylglycinate with vinyl alkanoate esters as highly effective antibacterial agents†
Abstract
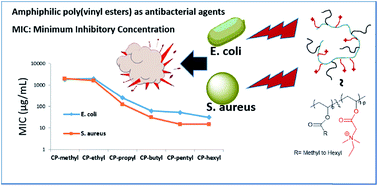
Synthetic amphiphilic poly(vinyl ester) copolymers of vinyl N,N-dimethylethylglycinate with vinyl alkanoate esters can show very high antibacterial activities. The copolymers contain a positive charge one carbon away from the ester group and alkane side chains in the size range from methyl to hexyl groups. A copolymer (degree of polymerization as 9) with 37 mole% of hexyl side chains showed high antibacterial activities in terms of minimum inhibitory concentrations (31 μg mL−1 against Escherichia coli and 16 μg mL−1 against Staphylococcus aureus) and an unusually high hemolytic activity. Compared with its isomeric polymethacrylates, this extremely high hemolytic power of poly(vinyl ester) can be attributed to its more accessible C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O dipole orientation for hydrogen bond formation and dipole–dipole interaction with the cell surface.
O dipole orientation for hydrogen bond formation and dipole–dipole interaction with the cell surface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...