New structures, chemotaxonomic significance and COX-2 inhibitory activities of cassane-type diterpenoids from the seeds of Caesalpinia minax†
Abstract
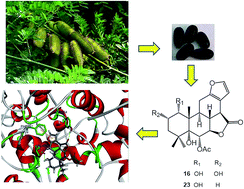
Eleven new cassane-type diterpenoids (1–11), along with 12 known compounds were isolated from the seeds of Caesalpinia minax Hance. Their structures were determined by extensive spectroscopic methods in combination with X-ray diffraction analysis. All the compounds were evaluated for COX-2 inhibitory activity, and displayed different levels of inhibition except for 14 whose C and D rings were connected through a spiro-atom. Among them, compound 23, a furanoditerpenoid lactone with a hydroxyl group at C-1 displayed the most potent inhibitory activity with an inhibition ratio of 82.0% at 4.0 μM, which was stronger than its analog 16 with an additional hydroxyl group at C-2. Further detailed testing showed that both compounds 23 and 16 dose-dependently inhibited the COX-2 enzyme with IC50 values of 2.4 ± 0.1 and 3.2 ± 0.2 μM, respectively. Molecular docking analysis showed significant hydrogen bonding and π–π interactions with the enzyme, and revealed the docking scores 36.3108 and 28.6678 for 23 and 16, respectively, which are consistent with their IC50 values. Cytotoxic assay showed that all these diterpenoids only exhibit weak activities with IC50 values over 50 μM on normal cells. Thus, these diterpenoids might be potential anti-inflammatory agents targeting the COX-2 enzyme with low toxicity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...