Amphipathic trans-acting phosphorothioate DNA elements mediate the delivery of uncharged nucleic acid sequences in mammalian cells†
Abstract
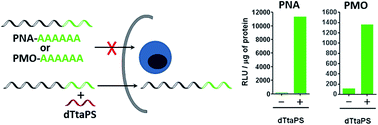
A convenient approach to the delivery of uncharged peptide nucleic acids (PNA) or phosphorodiamidate morpholino (PMO) oligomers in mammalian cells is presented and consists of extending the sequence of these oligomers with a short (6-mer) PNA-polyA or PMO-polyA tail. Recognition of the polyA-tailed PNA or PMO oligomers by an 8-mer amphipathic trans-acting polythymidylic thiophosphate triester element (dTtaPS) results in efficient internalization of these oligomers in several cell lines. Our findings indicate that internalization of the oligomers occurs through an energy-dependent mechanism and macropinocytosis appears to be the prevailing endocytic pathway used for cellular uptake. The functionality of the internalized oligomers is demonstrated by alternate splicing of the pre-mRNA encoding luciferase in HeLa pLuc 705 cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...