A Geobacter strain isolated from rice paddy soil with higher bioelectricity generation capability in comparison to Geobacter sulfurreducens PCA†
Abstract
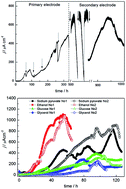
A novel electrochemically active strain D-8 was successfully isolated from rice paddy soil by combining primary enrichment on electrode, secondary biofilm selection on electrode via electrochemical consecutive selection, Fe(III)-oxide reduction, fumarate selection and a dilution–extinction plating technique. The maximum current density of 480 ± 5.5 μA cm−2 (n = 3) produced on primary biofilm increased to 1010 ± 0.4 μA cm−2 (n = 2) μA cm−2 after selection using Fe(III)-oxide, which showed that the paddy soil contained Fe(III)-reducing bacteria with a highly efficient electricity generation capability. In addition, phylogenetic analyses using the 16S rRNA gene sequence demonstrated that strain D-8 was most closely related to G. sulfurreducens PCA, with 99.53% sequence similarity. Meanwhile BOX-PCR, a rep-PCR technique, was used and provided obviously different genomic fingerprints between G. sulfurreducens and strain D-8 in some specific DNA fragments. Furthermore, strain D-8 also showed different physiological and biochemical characteristics from Geobacter sulfurreducens PCA. For example, strain D-8 is a facultative bacterium, and can use more carbon sources such as ethanol, glucose and sucrose than G. sulfurreducens PCA. These results implied that the two strains possessed distinguishable physiological, biochemical and nucleic acid characteristics. Especially, a strain D-8 biofilm on an electrode surface produced a 1.5 times higher current density of 1088 ± 7.7 μA cm−2 (n = 6) than G. sulfurreducens PCA (722 ± 2.6 μA cm−2, n = 4). Therefore, strain D-8 will be a promising bioanodic organism in microbial fuel cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...