Axially phenoxylated aluminum phthalocyanines and their application in organic photovoltaic cells†
Abstract
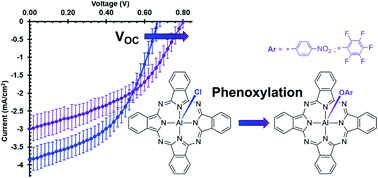
Novel axially phenoxylated aluminium phthalocyanines, pentafluorophenoxy aluminium phthalocyanine (F5PhO-AlPc) and p-nitrophenoxy aluminium phthalocyanine (NO2PhO-AlPc), were synthesized through a one-step reaction starting from the commonly used photoactive material, chloro aluminium phthalocyanine (Cl-AlPc), and the respective phenols. Reactions with other phenols did not yield corresponding AlPc derivatives. Optical, electrical, and thermal analyses were carried out on F5PhO-AlPc and NO2PhO-AlPc using UV-Vis measurements (solution and thin-film), cyclic voltammetry (CV), differential-pulse voltammetry (DPV), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). A simple thermodynamic model was used to explain the lack of reaction when Cl-AlPc was treated a variety of alkylated phenols. We noted a side reaction producing fluoro aluminium phthalocyanine (F-AlPc) when the synthesis of F5PhO-AlPc was attempted in DMF. The model also explains this observation. F5PhO-AlPc and NO2PhO-AlPc were integrated into organic photovoltaic devices (OPVs) both as electron-donating and as electron-accepting materials. The phenoxy-AlPcs enable an enhancement of the open-circuit voltage (VOC) of the OPVs when applied as either an electron donor or as an electron acceptor compared to Cl-AlPc. The results within the OPV, specifically the increased VOC, are consistent with the steric shielding effect seen in other OPVs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...