Experimental and theoretical study on dissolution of a single mixed gas bubble in a microalgae suspension†
Abstract
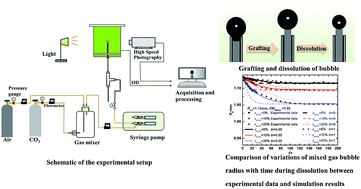
Aiming at technology for biofixation of carbon dioxide by microalgae in photobioreactors, a basic phenomenon, that is, the dissolution and consumption of a mixed gas bubble consisting of CO2 and air in a microalgae suspension, was investigated by visualization experiments using the promoted bubble grafting method. Furthermore, a theoretical model based on non-equilibrium theory at the gas–liquid interface was also proposed to predict the CO2 dissolution and fixation characteristics of bubbles in a microalgae suspension. The effects of the initial CO2 volume fraction, initial bubble size and microalgae concentration were discussed respectively. It was found that the bubble radius gradually decreased with time and trended towards a constant thereafter. The dimensionless Biot number in the promoted dissolution model was determined as 0.65 for the microalgae suspension. The bubble with a larger initial CO2 volume fraction experienced faster shrinkage and had a higher dissolution rate and CO2 fixation efficiency, while slight photosynthesis inhibition emerged at the beginning of dissolution when the initial CO2 volume fraction in the bubble was larger than 15%. A smaller initial bubble size resulted in a lower dissolution rate but greater CO2 fixation efficiency by photosynthesis. Higher microalgae concentration facilitated bubble dissolution and CO2 fixation especially when OD680 nm of the microalgae suspension was less than 1.0. These findings can be a guide to the design of a photobioreactor and aerator.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...