Effect of finite ion sizes in electric double layer mediated interaction force between two soft charged plates
Abstract
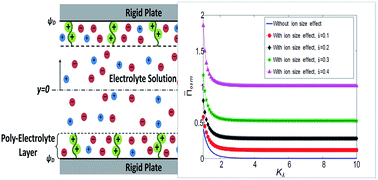
We present a theory to compute the electric-double-layer (EDL) mediated per unit area interaction force, or the osmotic pressure, between two soft charged plates separated by a thin layer of electrolyte solution with and without the consideration of finite ion sizes or finite steric effect. These soft charged plates are represented by a charged polyelectrolyte layer (PEL) sandwiched between a rigid plate and an electrolyte solution. The thickness of this PEL is considered to be independent of the EDL effects, rather being governed by the balance of the elastic and the volume exclusion effects of the polyelectrolyte chain. The PEL-rigid-solid interface is considered as uncharged. We provide closed-form analytical results to demonstrate that for a given concentration of electrolyte ions, the osmotic pressure depends solely on two parameters: first, the ratio of the Debye length to a thickness that quantifies the charge content of the PEL, and second, the steric factor quantifying the ion size or steric effect. More importantly, we discover a hidden relationship that connects this ratio of the two thicknesses to the dimensionless Debye length and the dimensionless PEL thickness. This relationship ensures that the osmotic pressure does depend on the plate separation. Finally, we show that the steric effect substantially augments the osmotic pressure, attributed to the corresponding increase in the electrostatic potential at the PEL-rigid-plate interface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...