Cadmium induced apoptosis in mouse primary hepatocytes: the role of oxidative stress-mediated ERK pathway activation and the involvement of histone H3 phosphorylation†
Abstract
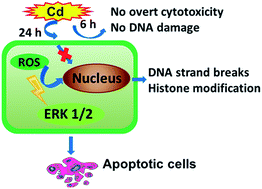
Cadmium can disturb the intracellular redox state and generate oxidative stress, leading to a variety of diseases. A number of studies have reported that oxidative stress and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways contributes to the induction or inhibition of apoptosis, depending on the types of cell lines and stimulus. However, the role of oxidative stress and the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathways in the apoptosis of cadmium-treated primary hepatocytes and its underlying mechanism still remain unclear. The present study clearly confirms the important role of oxidative stress in the time-delayed effects of cadmium-induced apoptosis. Rather than direct induction by cadmium, cadmium decreased cell viability by causing oxidative stress mediated-apoptosis after 24 h exposure. This was verified by the persistent elevation of excessive reactive oxygen species and DNA oxidative damage, the decrease in glutathione level and the protection of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC). Furthermore, NAC and PD98059 prevented apoptosis, caspase-3 activation and histone H3 phosphorylation. Also, NAC suppressed Cd-induced activation of the ERK pathway. These results demonstrated that oxidative stress-regulated downstream ERK pathway activation plays a pivotal role in Cd-induced apoptosis of primary hepatocytes. The present study also indicates for the first time that Cd-induced histone H3 phosphorylation is closely associated with activation of the ERK pathway and is involved in oxidative stress-mediated DNA damage and cell death. These results will contribute to a better understanding of the cellular mechanisms of cadmium toxicity and its effects on human health.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...