Investigation of interfacial and photoelectrochemical characteristics of thermally treated PbS/TiO2 photoanodes†
Abstract
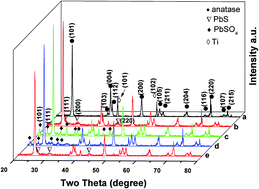
Photoanodes composed of PbS QD sensitized TiO2 nanotube arrays (PbS/TNAs) were prepared via the series ion layer adsorption replacement (SILAR) method. The samples were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), UV-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-vis DRS), and photoluminescence (PL) to illustrate the sample microscopic morphologies, chemical composition, and light absorption properties. Current–potential (J–V), current–time (I–t), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and Mott–Schottky analyses revealed the charge transport and interfacial features in the samples. The effects of thermal treatments on PbS/TNAs interfacial contact and photoelectrochemical properties were systematically investigated. Under different atmospheres (air, vacuum, N2) during the thermal treatment, the crystal phase and chemical composition, light absorption, PbS quantum dot size and exposed crystal face, flat band potential, and resistance traits changed accordingly. When the sample was heated in N2, some of the PbS QDs were oxidized to form a PbS@PbSO4 junction. The size of the quantum dots increased from 4–5 nm to 14–15 nm, and the exposed crystal face changed from {111} to {200}. The interfacial resistances between PbS and TiO2 increased as well. When the samples were thermally treated in air or vacuum, PbS QDs were mostly oxidized to PbSO4. After the electrodes were immersed in sulfur-containing electrolyte, PbSO4 was vulcanized to PbS. Due to the limited mass transport across the newly formed PbS layer, the reduction was hardly complete. A PbSO4@PbS junction was formed with the new PbS having an exposed crystal face of {220} instead of {111}. The sample not thermally treated boasted the best photoelectrochemical features with a short circuit current density of 7.04 mA cm−2. The sample thermally treated in N2 embraced the worst photoelectrochemical traits with a short circuit current density of 3.0 mA cm−2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...