Ni–P synergetic deposition: electrochemically deposited highly active Ni as a catalyst for chemical deposition†
Abstract
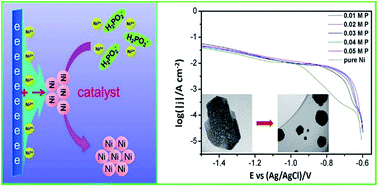
The nucleation mechanism of the preparation of a Ni–P deposit by the synergetic effect of electrochemical deposition and chemical deposition was studied using an electrochemical analysis method. Cathode polarization and chronoamperometry were performed to explore the effect of the reducing reaction (chemical deposition) on the electrochemical Ni deposition. It was found that the addition of reducing agent to the solution induced depolarization phenomena and decreased or removed the double electric layer capacitance. The chronoamperometry experimental data were analyzed and fitted according to the Scharifker–Hills rule to discover the difference in mechanism between the Ni nucleation and Ni–P nucleation. The morphology of Ni–P and the pure Ni deposits was measured by TEM and SEM demonstrating the ball-like particle shape of Ni–P and flat pure Ni deposits. Based on these experimental results, the nucleation mechanism was illustrated in which the active Ni atoms, produced by electrochemical deposition, act as a catalyst for the reduction of the nickel ions with the reducing agent NaH2PO2 on the cathode surface. The occurrence of the reducing reaction of the nickel ions with NaH2PO2 hindered the in-plane growth of crystalline nickel particles, generating the ball-like particle shape of the deposit. This work provides researchers new insights into the nucleation and growth process of synergetic deposition and offers novel ideas for the fabrication of functional materials by liquid deposition.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...