Enhancing aerobic digestion of full-scale waste activated sludge using free nitrous acid pre-treatment
Abstract
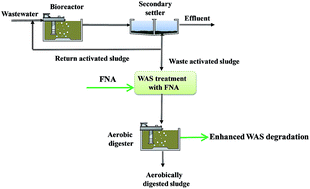
Aerobic digestion is one of the mainstream technologies for waste activated sludge (WAS) reduction and stabilization prior to disposal, but its effectiveness is limited by the poor degradation of WAS. This study presents a novel strategy based on free nitrous acid (FNA i.e. HNO2) pre-treatment to enhance full-scale WAS degradation in aerobic digestion. The full-scale WAS was subject to FNA treatment at 2.0 mg HNO2–N per L for 24 h. The degradation of the FNA-treated WAS was then compared to that of the same WAS without FNA pre-treatment by aerobically digesting the WAS with a full-scale activated sludge for 14 days. Approximately 50% of the FNA-treated WAS was degraded during the 14 day aerobic digestion compared to 32% achieved with the untreated WAS. The inorganic nitrogen production (originating from breakdown of WAS) from the FNA-treated WAS was 43 mg N per g of mixed liquor volatile suspended solids (MLVSS) in the 14 day aerobic digestion, whereas its production from the untreated WAS was only 29 mg N per g of MLVSS, confirming the effectiveness of the FNA pre-treatment in enhancing aerobic digestion of full-scale WAS. Economic analysis showed that the FNA pre-treatment method was economically attractive, saving a cost of %-15 500–64 500 per year depending on WAS disposal cost in a treatment plant with a population equivalent of 80 000.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...