Palladium-catalyzed oxidative annulation of in situ generated enones to pyrroles: a concise route to functionalized indoles†
Abstract
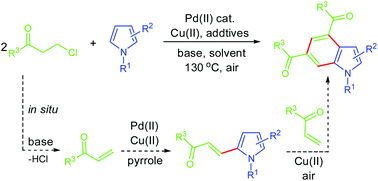
Palladium(II)-catalyzed, copper(II)-mediated indole synthesis was achieved from the reactions of N-substituted simple pyrroles with enones generated in situ from 3-chloropropiophenones. A benzene ring was thus constructed onto a pyrrole backbone, affording substituted indole derivatives. A domino dehydrochlorination/C–H olefination /Diels–Alder cycloaddition/dehydrogenative aromatization sequence was established as the reaction pathway. The present methodology provides a concise route to highly functionalized indole derivatives.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...