Thermoresponsive, well-defined, poly(vinyl alcohol) co-polymers†
Abstract
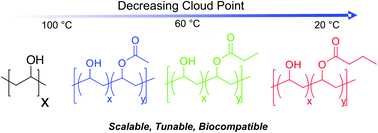
Thermoresponsive polymers have attracted huge interest as adaptable biomaterials based on their reversible solubility behaviour which can be exploited for controlled drug delivery or cellular uptake. The most famous and successful of these is poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), but the thermal transition temperatures that are practically accessible are not physiologically useful. There are some notable examples of synthetic, responsive, polymers that are highly tunable over a physiologically relevant range, but there is still a need for these to be clinically validated in terms of toxicology and immunogenity for in vivo usage, in addition to their widely used in vitro applications. Poly(vinyl alcohol), PVA, is an appealing biocompatible polymer which is already used for a huge range of biomedical applications. Here, PVA is shown to be a highly tunable, thermoresponsive polymer scaffold. RAFT/MADIX polymerization is used to obtain a library of well-defined polymers between 8 and 50 kDa. Selective alkanoylation of the obtained PVA enabled the effect of side-chains, end-groups and molecular weight on the observable transition temperatures to be studied by turbidimetry. It was found that increasingly hydrophobic side chains (acetyl, propanoyl, butanoyl), or increasing their density led to corresponding decreases in cloud point. PVA with just 10 mol% butanoylation was shown to have a thermal transition temperature close to physiological temperatures (37 °C), compared to 70 mol% for acetylation, with temperatures in between accessible by controlling both the relative degree of functionalization, or by altering the chain length. Finally, a secondary response to esterase enzymes was demonstrated as a route to ‘turn off’ the responsive behaviour on demand. This study suggests that PVA-derived polymers may be a useful platform for responsive biomaterials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...