Retracted Article: Influence of 2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl methacrylate on acid-triggered hydrolysis of cyclic benzylidene acetals and their importance in efficient drug delivery†
Abstract
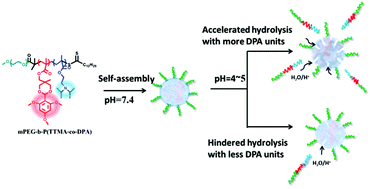
The ability to tune the degradation rate of a biodegradable polymer, which can achieve precise spatiotemporal control of drug delivery, is of considerable interest for biomedical applications. In this study, a series of amphiphilic copolymers, methoxy poly(ethyleneglycol)-b-poly((2,4,6-trimethoxybenzylidene-1,1,1-tris(hydroxymethyl) ethane methacrylate)-co-2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (mPEG-b-P(TTMA-co-DPA), PETD) with different numbers of DPA units, were synthesized by Reversible Addition Fragmentation Chain Transfer (RAFT) copolymerization, in which DPA containing tertiary amines were introduced to adjust the hydrolysis behavior of cyclic benzylidene acetals (CBAs). The molecular structure and the chemical composition of PETD were characterized by 1H NMR and gel permeation chromatography (GPC). PETD could self-assemble into stable nanoparticles with well-defined spherical morphology and displayed high drug loading capacity with doxorubicin (DOX) as the drug model. The hydrolysis behavior of CBAs in the PETD NPs was investigated by UV/vis spectroscopy under different pH values. Compared with PETD-0 bearing no DPA unit, the hydrolysis rate of PETD-3 with more DPA was faster, while PETD-1 with less DPA hydrolyzed much slower, which indicated that the introduction of DPA had an amphoteric effect on the hydrolysis behavior of CBAs under acidic conditions. In addition, the in vitro release of DOX was also investigated under different pH conditions and the result was in accordance with the hydrolysis result. Furthermore, the results of fluorescence microscopy demonstrated improved internalization of DOX-loaded PETD-3 NPs in HepG-2 cells with rapid DOX release intracellularly, which showed considerable cytotoxicity against HepG-2 cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...