Synthesis and bioactivity of a conjugate composed of green tea catechins and hyaluronic acid†
Abstract
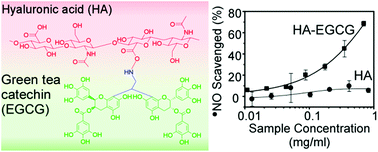
(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is a green tea polyphenol that has several biological activities, including anti-cancer activity and anti-inflammation. Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally-occurring polysaccharide that is widely used as a biomaterial for drug delivery and tissue engineering due to its viscoelastic, biocompatible and biodegradable properties. By conjugating HA with EGCG, the resulting HA–EGCG conjugate is expected to exhibit not only the inherent properties of HA but also the bioactivities of EGCG. Toward this end, we report the synthesis of an amine-functionalized EGCG as an intermediate compound for conjugation to HA. EGCG was reacted with 2,2-diethoxyethylamine (DA) under acidic conditions, forming ethylamine-bridged EGCG dimers. The EGCG dimers were composed of four isomers, which were characterized by HPLC, high-resolution mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy. The amine-functionalized EGCG dimers were conjugated to hyaluronic acid (HA) through the formation of amide bonds. HA–EGCG conjugates demonstrated several bioactivities which were not present in unmodified HA, including resistance to hyaluronidase-mediated degradation, inhibition of cell growth and scavenging of radicals. The potential applications of HA–EGCG conjugates are discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...