Halogenated quinolines discovered through reductive amination with potent eradication activities against MRSA, MRSE and VRE biofilms†
Abstract
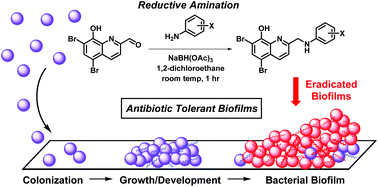
Small molecules capable of eradicating non-replicating bacterial biofilms are of great importance to human health as conventional antibiotics are ineffective against these surface-attached bacterial communities. Here, we report the discovery of several halogenated quinolines (HQs) identified through a reductive amination reaction that demonstrated potent eradication of MRSA (HQ-6; MBEC = 125 μM), MRSE (HQ-3; MBEC = 3.0 μM) and VRE (HQ-4, HQ-5 and HQ-6; MBEC = 1.0 μM) biofilms. HQs were evaluated using the Calgary Biofilm Device (CBD) and demonstrated near equipotent killing activities against planktonic and biofilm cells based on MBC and MBEC values. When tested against red blood cells, these HQ analogues demonstrated low haemolytic activity (3 to 21% at 200 μM) thus we conclude that these HQ analogues do not operate primarily through the destruction of bacterial membranes, typical of other biofilm-eradicating agents (i.e., antimicrobial peptides). HQ antibacterial agents are potent biofilm-eradicating compounds and could lead to useful treatments for biofilm-associated bacterial infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...