Fluorescent organic nanoparticles of dihydropyrimidone derivatives for selective recognition of iodide using a displacement assay: application of the sensors in water and biological fluids†
Abstract
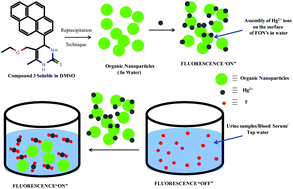
Fluorescent organic nanoparticles (FON's) derived from dihydropyrimidone derivatives (1–4) were developed and evaluated for their sensor properties. Nano-aggregates of compound 3 and 4 resulted in sensors. Nano-aggregates of compound 3 showed enhancement in the monomer peaks of the pyrene moiety after the addition of mercury. Nano-aggregates of compound 4 resulted in quenching of intensity upon addition of Hg2+. On the other hand, no sensor activity was recorded for nano-aggregates of compounds 1 and 2. Further, the complex of nano-aggregates of 3 and mercury (3·Hg2+) recognised iodide ions by showing quenching in monomer and excimer emission with a detection limit of 0.2 nM in aqueous medium; however the resultant metal complex 4·Hg2+ does not show any anion sensing activity. Receptor 3·Hg2+ has a highly sensitive and selective response toward I− ions. Therefore, the iodide content of tap water, urine and blood serum is monitored using this sensor and it is found that the sensor can detect a range of iodide in tap water, urine and blood serum. To the best of our knowledge, the system represents the first example of iodide recognition using FONs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...