Ionizing radiation improves glioma-specific targeting of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles conjugated with cmHsp70.1 monoclonal antibodies (SPION–cmHsp70.1)†
Abstract
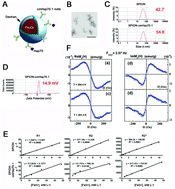
The stress-inducible 72 kDa heat shock protein Hsp70 is known to be expressed on the membrane of highly aggressive tumor cells including high-grade gliomas, but not on the corresponding normal cells. Membrane Hsp70 (mHsp70) is rapidly internalized into tumor cells and thus targeting of mHsp70 might provide a promising strategy for theranostics. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) are contrast negative agents that are used for the detection of tumors with MRI. Herein, we conjugated the Hsp70-specific antibody (cmHsp70.1) which is known to recognize mHsp70 to superparamagnetic iron nanoparticles to assess tumor-specific targeting before and after ionizing irradiation. In vitro experiments demonstrated the selectivity of SPION–cmHsp70.1 conjugates to free and mHsp70 in different tumor cell types (C6 glioblastoma, K562 leukemia, HeLa cervix carcinoma) in a dose-dependent manner. High-resolution MRI (11 T) on T2-weighted images showed the retention of the conjugates in the C6 glioma model. Accumulation of SPION–cmHsp70.1 nanoparticles in the glioma resulted in a nearly 2-fold drop of 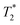 values in comparison to non-conjugated SPIONs. Biodistribution analysis using NLR-M2 measurements showed a 7-fold increase in the tumor-to-background (normal brain) uptake ratio of SPION–cmHsp70.1 conjugates in glioma-bearing rats in comparison to SPIONs. This accumulation within Hsp70-positive glioma was further enhanced after a single dose (10 Gy) of ionizing radiation. Elevated accumulation of the magnetic conjugates in the tumor due to radiosensitization proves the combination of radiotherapy and application of Hsp70-targeted agents in brain tumors.
values in comparison to non-conjugated SPIONs. Biodistribution analysis using NLR-M2 measurements showed a 7-fold increase in the tumor-to-background (normal brain) uptake ratio of SPION–cmHsp70.1 conjugates in glioma-bearing rats in comparison to SPIONs. This accumulation within Hsp70-positive glioma was further enhanced after a single dose (10 Gy) of ionizing radiation. Elevated accumulation of the magnetic conjugates in the tumor due to radiosensitization proves the combination of radiotherapy and application of Hsp70-targeted agents in brain tumors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...