Probing individual point defects in graphene via near-field Raman scattering
Abstract
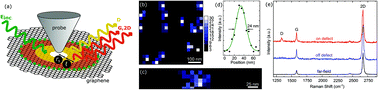
The Raman scattering D-peak in graphene is spatially localised in close proximity to defects. Here, we demonstrate the capability of tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) to probe individual point defects, even for a graphene layer with an extremely low defect density. This is of practical interest for future graphene electronic devices. The measured TERS spectra enable a direct determination of the average inter-defect distance within the graphene sheet. Analysis of the TERS enhancement factor of the graphene Raman peaks highlights the preferential enhancement and symmetry-dependent selectivity of the D-peak intensity caused by zero-dimensional Raman scatterers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...