MicroRNA-triggered, cascaded and catalytic self-assembly of functional “DNAzyme ferris wheel” nanostructures for highly sensitive colorimetric detection of cancer cells
Abstract
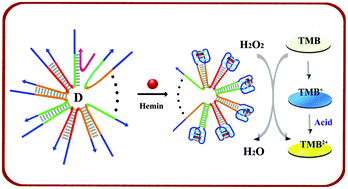
The construction of DNA nanostructures with various sizes and shapes has significantly advanced during the past three decades, yet the application of these DNA nanostructures for solving real problems is still in the early stage. On the basis of microRNA-triggered, catalytic self-assembly formation of the functional “DNAzyme ferris wheel” nanostructures, we show here a new signal amplification platform for highly sensitive, label-free and non-enzyme colorimetric detection of a small number of human prostate cancer cells. The microRNA (miR-141), which is catalytically recycled and reused, triggers isothermal self-assembly of a pre-designed, G-quadruplex sequence containing hairpin DNAs into “DNAzyme ferris wheel”-like nanostructures (in association with hemin) with horseradish peroxidase mimicking activity. These DNAzyme nanostructures catalyze an intensified color transition of the probe solution for highly sensitive detection of miR-141 down to 0.5 pM with the naked eye, and the monitoring of as low as 283 human prostate cancer cells can also, theoretically, be achieved in a colorimetric approach. The work demonstrated here thus offers new opportunities for the construction of functional DNA nanostructures and for the application of these DNA nanostructures as an effective signal amplification means in the sensitive detection of nucleic acid biomarkers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...