Highly sensitive detection for proteins using graphene oxide-aptamer based sensors†
Abstract
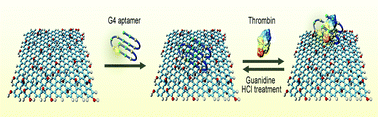
In recent years, the detection of proteins by using bare graphene oxide (GO) to quench the fluorescence of fluorescein-labeled aptamers has been reported. However, the proteins can be adsorbed on the surface of bare GO to prevent the sensitivity from further being improved. In order to solve this problem, polyethylene glycol (PEG)-protected GO was used to prevent the proteins using thrombin as an example from nonspecific binding. The detection limit was improved compared to bare GO under the optimized ratio of GO to PEG concentration. The results show that our method is a promising technique for the detection of proteins.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...