99mTc radiolabelling of Fe3O4–Au core–shell and Au–Fe3O4 dumbbell-like nanoparticles†
Abstract
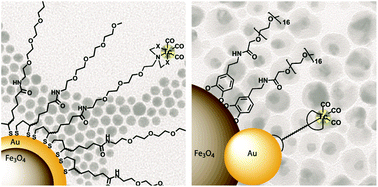
The development of nanoparticle-based dual-modality probes for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) or single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is increasingly growing in importance. One of the most commonly used radionuclides for clinical SPECT imaging is 99mTc and the labelling of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with 99mTc was shown to be a successful strategy to obtain dual-modality imaging agents. In this work, we focus on gold containing magnetic nanomaterials. The radiolabelling of magnetic Fe3O4–Au core–shell and Fe3O4–Au dumbbell-like nanoparticles with the [99mTc(CO)3]+ fragment is described. The key elements for this 99mTc labelling approach are novel coating ligands, consisting of an anchor for the Au surface, a polyethylene glycol linker and a strong chelator for the [99mTc(CO)3]+ moiety.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...