Hybridized doxorubicin-Au nanospheres exhibit enhanced near-infrared surface plasmon absorption for photothermal therapy applications†
Abstract
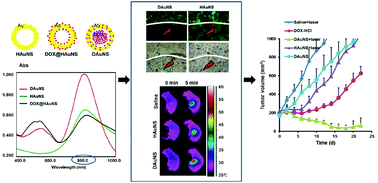
Photothermal therapy (PTT) employs photosensitizing agents, which are taken up by cells and generate heat when irradiated with near-infrared (NIR) light, to enable the photoablation of cancer cells. High absorption in the NIR region is crucial for a photosensitizing agent to achieve efficient PTT. Different combinations between gold nanoparticles and fluorescent agents always influence their spectrum properties. Herein, we fabricated a novel combination of a fluorescent agent (doxorubicin, DOX, also a popular chemotherapeutic agent) with gold nanospheres by synthesizing hybridized DOX-Au nanospheres (DAuNS), where a part of the DOX molecules and Au co-formed a hybridized matrix as the shell and the remaining DOX molecules precipitated as the core. The unique structure of DAuNS induced interesting changes in the characteristics including spectrum properties, morphology, drug loading and antitumor activity. We observed that DAuNS exhibited a significantly enhanced surface plasmon absorption in the NIR region, inducing a more efficient photothermal conversion and stronger tumor-cell killing ability under NIR laser irradiation. In addition, our study presents a new and simple platform to load a drug into nanoparticles. DAuNS could be a promising nanoparticle with the “two punch” efficacy of PTT and chemotherapy and could be used in clinical applications due to its controllable synthesis, small size, and narrow size distribution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...