Edge reconstruction-mediated graphene fracture
Abstract
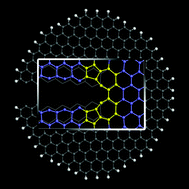
Creation of free edges in graphene during mechanical fracture is a process that is important from both fundamental and technological points of view. Here we derive an analytical expression for the energy of a free-standing reconstructed chiral graphene edge, with chiral angle varying from 0° to 30°, and test it by first-principles computations. We then study the thermodynamics and kinetics of fracture and show that during graphene fracture under uniaxial load it is possible to obtain fully reconstructed zigzag edges through sequential reconstructions at the crack tip. The preferable condition for this process is high temperature (T ∼ 1000 K) and low (quasi-static) mechanical load (KI ∼ 5.0 eV Å−5/2). Edge configurations of graphene nanoribbons may be tuned according to these guidelines.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...