Incident angle–tuned, broadband, ultrahigh-sensitivity plasmonic antennas prepared from nanoparticles on imprinted mirrors†
Abstract
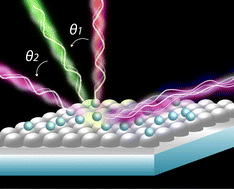
We have used a direct imprint-in-metal method that is cheap and rapid to prepare incident angle–tuned, broadband, ultrahigh-sensitivity plasmonic antennas from nanoparticles (NPs) and imprinted metal mirrors. By changing the angle of incidence, the nanoparticle-imprinted mirror antennas (NIMAs) exhibited broadband electromagnetic enhancement from the visible to the near-infrared (NIR) regime, making them suitable for use as surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)–active substrates. Unlike other SERS-active substrates that feature various structures with different periods or morphologies, the NIMAs achieved broadband electromagnetic enhancement from single configurations. The enhancement of the electric field intensity in the NIMAs originated from coupling between the localized surface plasmon resonance of the NPs and the periodic structure-excited surface plasmon resonance (SPR) of the imprinted mirror. Moreover, the coupling wavelengths could be modulated because the SPR wavelength was readily tuned by changing the angle of the incident light. Herein, we demonstrate that such NIMAs are robust substrates for visible and NIR surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering under multiple laser lines (532, 633, and 785 nm) of excitation. In addition, we have found that NIMAs are ultrasensitive SERS-active substrates that can detect analytes (e.g., rhodamine 6G) at concentrations as low as 10−15 M.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...