A restriction enzyme-powered autonomous DNA walking machine: its application for a highly sensitive electrochemiluminescence assay of DNA†
Abstract
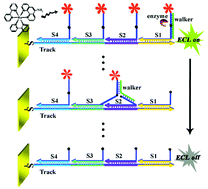
The construction of a restriction enzyme (Nt.AlwI)-powered DNA walking machine and its application for highly sensitive detection of DNA are described. DNA nanostructure tracks containing four overhang sequences with electrochemiluminescence (ECL) labels and complementary to the walker (target DNA) are self-assembled on the sensing electrode. The walker hybridizes with the complementary sequences on the tracks and forms specific recognition sites for Nt.AlwI, which cleaves the overhang sequences, releases the ECL labels and enables directional movement of the walker along the tracks. The formation of the nanostructure tracks and the Nt.AlwI-assisted cleavage of the overhang sequences in the presence of the walker are verified by using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis and cyclic voltammetry. The successive movement of the walker on the nanostructure tracks leads to continuous removal of massive ECL labels from the sensing electrode, which results in a significantly amplified suppression of the ECL emission for highly sensitive detection of sequence-specific DNA down to 0.19 pM. Results show that this DNA walking machine can also offer single-base mismatch discrimination capability. The successful application of the DNA walking machine for sequence-specific DNA detection can thus offer new opportunities for molecular machines in biosensing applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...