Studies on the thymine–mercury–thymine base pairing in parallel and anti-parallel DNA duplexes†
Abstract
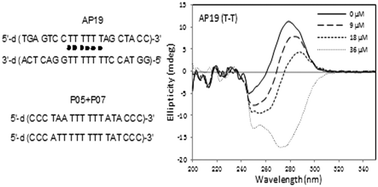
The stable T–Hg–T base pair in nucleic acids has been widely applied for Hg2+ biosensors. Based on the N–Hg binding mechanism for a mercury ion to nucleobases, the N–Hg–N bond was studied in other base pairs (T–T, T–G, G–G, C+–C+) with two imino groups within the base pairing face, in the context of parallel DNA duplexes. In the six C+–C+ pairs – defined parallel DNA duplexes at pH 5.0, the parallel T–Hg–T was suggested to be a very weak base pair, as it was not stable enough to support a long T–Hg–T stem, unlike the anti-parallel T–Hg–T base pair. No interactions between Hg2+ and the parallel T–G, G–G, and C+–C+ pairs were observed. In the anti-parallel dsDNA, the stabilizing effect of T–Hg–T was significant, but with position and sequence dependence, it was mostly less stable than the natural A–T base pair. An anti-parallel T–Hg–T stem is preferred over a parallel stem in the functional nucleic acids for the design of Hg2+ biosensors. It seems that the N–Hg–N bond is only accommodated in the T–T pair within the DNA duplex, different from the free bonding mode between individual nucleobases, nucleosides, or nucleotides. These results are helpful for the design of the T–Hg–T stem in Hg2+ biosensors based on functional nucleic acids.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...