The role of Cu species in electrospun CuO–CeO2 nanofibers for total benzene oxidation
Abstract
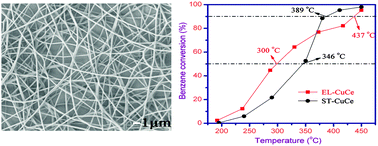
CuO–CeO2 nanofibers with relatively high surface area (EL-CuCe) have been successfully prepared by the electrospinning method and investigated for total benzene oxidation. The improved low-temperature performance of EL-CuCe compared to ST-CuCe (prepared by the surfactant-templated method) is attributed to the better reducibility of Cu ions that are incorporated into the ceria lattice. Moreover, more oxygen vacancies and weakly bound oxygen species (e.g., O2−, O22− or O−) observed on EL-CuCe keep in step with its higher low-temperature oxidation activity. However, without small amounts of bulk CuO, reduction of some surface ceria occurs at 480 °C for EL-CuCe, which probably accounts for its unsatisfactory high temperature performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...