Effect of pretreatment temperature on the photocatalytic activity of microwave irradiated porous nanocrystalline ZnO†
Abstract
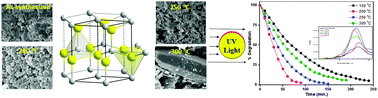
Porous nanocrystalline ZnO photocatalysts were successfully synthesized by microwave irradiation and then thermally treated at different temperatures (150 °C, 200 °C, 250 °C and 300 °C). The physico-chemical properties of synthesized samples were determined by using different characterization techniques. The characterization results indicated that the as-synthesized sample was comprised of both ZnO and Zn(OH)2 phases with a particle size of approximately 50 nm. Thermal treatment of the as-synthesized sample at 150 °C resulted in a pure ZnO phase with a particle size of 40 nm. The results also demonstrated that the surface area, pore diameter and bandgap energy reach a maximum value for the ZnO sample treated at 200 °C. The ZnO nanoparticles pretreated at 200 °C showed the highest photocatalytic activity (99% of degradation) in a short reaction time (90 min), which can be attributed to the combined effects of several factors including low crystallite size, relatively high surface area, pore diameter, pore volume and bandgap energy. Reusability results show that the catalysts can be readily separated from the reaction mixture by filtration after the photocatalytic reaction and reused at least five times without any loss of activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...