Insights into the impact of N- and O-methylation on aqueous solubility and lipophilicity using matched molecular pair analysis†
Abstract
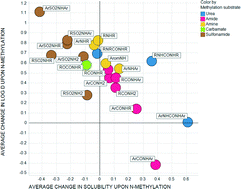
The impact of N- and O-methylation on chromatographically measured lipophilicity and high throughput chemiluminescent nitrogen detection (CLND) aqueous solubility was studied using matched molecular pairs for data sets of amides, sulfonamides, ureas, carbamates, amines, carboxylic acids, alcohols and phenols. The extent to which solubility and lipophilicity are affected by N- or O-methylation is dependent on the nature of atoms and substituents around the nitrogen or oxygen atom. In some classes of amides, N-methylation unexpectedly increases solubility and lowers log D7.4 considerably: this behaviour can be rationalised by conformational changes accompanying N-methylation that increase polar surface area, or by the disruption of one or more intramolecular hydrogen bonding motifs. Unlike amides, sulfonamide N-methylation always reduces solubility and increases lipophilicity, which again can be understood in terms of conformational effects. As expected, methylation of carboxylic acids lowers solubility and increases lipophilicity due to masking of the ionisable acidic group; however the magnitude of the reduction in solubility depends to some extent on the lipophilicity and molecular weight of the compound pairs under investigation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...