Novel quinoline derivatives as potent in vitro α-glucosidase inhibitors: in silico studies and SAR predictions†
Abstract
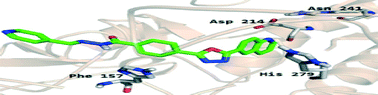
A new series of quinoline derivatives 6–30 was identified as potent α-glucosidase inhibitors. These analogs exhibited inhibitory potentials (IC50 values) in the ranges between 2.60 and 102.12 μM. Among the series, compounds 24 (2.60 ± 0.01 μM), 27 (2.60 ± 0.01 μM) and 20 (2.86 ± 0.01 μM) were found to be exceptionally potent (>14 times the standard) inhibitors of α-glucosidase when compared to the standard acarbose (IC50 = 38.25 ± 0.12 μM). Molecular docking studies on the two most active compounds 24 and 27 corroborated that compound 24 adopted a linear position to optimally fit into the binding site of α-glucosidase. Observations for the best position of compound 24 showed a total of four interactions towards catalytically active site residues of α-glucosidase involving amino acid residues such as Phe-177 and Asp-214. The oxadiazole ring of compound 24 interacted with His-279. Compound 27 formed one hydrogen bond interaction (N-methylacetamide) and three arene–arene interactions (quinoline and 1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety). The quinoline moiety of compound 27 formed two π-interactions with Phe-157. All compounds were tested for cytotoxicity, but none of them was found to be cytotoxic.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...