Discovery of high affinity inhibitors of Leishmania donovani N-myristoyltransferase†
Abstract
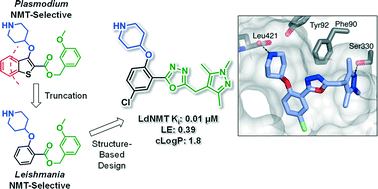
N-Myristoyltransferase (NMT) is a potential drug target in Leishmania parasites. Scaffold-hopping from published inhibitors yielded the serendipitous discovery of a chemotype selective for Leishmania donovani NMT; development led to high affinity inhibitors with excellent ligand efficiency. The binding mode was characterised by crystallography and provides a structural rationale for selectivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...