Aryl-imidazothiadiazole analogues as microtubule disrupting agents
Abstract
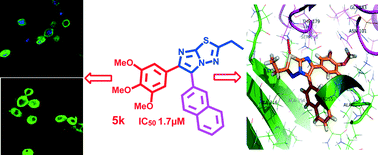
Two series of 2-ethyl-6-(3′,4′,5′-trimethoxyphenyl)-5-aryl and 2-cyclopropyl-6-(3′,4′,5′-trimethoxyphenyl)-5-aryl-imidazothiadiazoles were designed, synthesized and evaluated for anti-proliferative activity in various human cancer cell lines. A common starting material 2-bromo-1-(3-,4-,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-ethanone was employed to generate the two scaffolds. Among them, compounds functionalized with N,N-dimethylaniline (5i and 6i) and napthyl (5k) groups showed significant cytotoxic activity with average IC50 values of 1.7–2.9 μM, respectively. Moreover, the structure–activity relationship was elucidated by incorporating the different substitutions on the aryl moiety at the 5th position of the imidazothiadiazole ring. Treatments with 5i, 6i and 5k arrested cells at the G2/M phase, with cell death proceeding through an apoptotic pathway that was dependent on the activation of caspase-3. Immunocytochemical analysis revealed the loss of intact microtubule structures in treated cells. Treatments with 5i, 6i and 5k manifested increased mRNA and protein levels of the G2/M marker, cyclin B1. Molecular docking studies of the most potent compounds 5i, 5k and 6i showed that these compounds interact and bind efficiently to the active site of tubulin. This was further confirmed by a colchicine competitive binding assay.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...