Selective neuronal targeting, protection and signaling network analysis via dopamine-mediated mesoporous silica nanoparticles†
Abstract
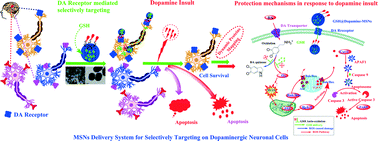
Neuronal transmitters specifically recognize and bind to receptors and have critical physical and pathological roles in neuronal functions. The possibility of using neurotransmitters as targeting ligands for drug delivery to the central nervous system (CNS) in nanoparticles has yet to be investigated. To examine the potential of neurotransmitter ligands to target specific neuronal groups, we grafted dopamine onto mesoporous silica nanoparticles (DA-MSNs), which enabled highly specific targeting of dopaminergic neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells, but not dopamine receptor (DAR)-negative cells (HEK293). Antioxidant peptide glutathione (GSH)-loaded DA-MSNs exhibited higher efficacy, as shown by the selectively protective effects against dopamine toxicity via the delivery of GSH into dopaminergic cells. Moreover, quantitative mass spectrometry analysis was employed to uncover the dynamic map of proteome changes with/without treatment GSH-loaded MSN@DA treatment. Several biological pathways were re-wired from proteome interaction networks and revealed important molecules underlying the cellular apoptosis caused by dopamine toxicity. These results provide not only a novel way to selectively target specific neuronal groups, such as dopaminergic neurons, but also a new tool to ultimately explore cellular mechanism of diseases involved in various neurological conditions via analysis of intracellular biochemical signaling cascades.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...