Amphotericin B and anidulafungin directly interact with DNA and induce oxidative damage in the mammalian genome†
Abstract
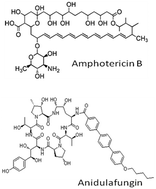
Amphotericin B and anidulafungin are widely used antifungal drugs for the treatment of systemic and serious mycoses. Amphotericin B is a relatively toxic drug which has long been established. This study is first of its kind to systematically investigate the nature of binding to DNA, and to evaluate intercalation of AMP-B or ANIDULA with the aid of UV-Vis, ITC, and CD spectroscopy. The binding affinity of AMP-B with exclusion sites of 4.68 base pairs (1.2 × 105 M−1) was found to be higher than that of ANIDULA with exclusion sites of 6.67 base pairs (3.78 × 104 M−1); consistent with the binding affinity values obtained for AMP-B (105 M−1) and ANIDULA (104 M−1). The binding of two drugs with double-stranded DNA was favoured by negative enthalpy as well as negative entropy changes. The intercalation of drugs to duplex polynucleotide induced changes in the intrinsic CD spectra and revealed comparatively higher affinity towards AMP-B than ANIDULA. Molecular docking studies revealed that the negative binding energy was higher in the case of AMP-B reflecting more affinity towards single-stranded DNA. The results of the cytotoxicity, immunoblotting, and gene specific LA-QPCR assay have indicated that ANIDULA is less genotoxic than AMP-B. Hence, the superiority of ANIDULA over AMP-B as a systemic antifungal drug has been established beyond doubt.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...