Over-expression of EPS15 is a favorable prognostic factor in breast cancer†
Abstract
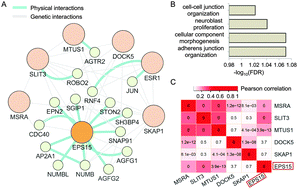
As a crucial player in terminating growth factor signaling, EPS15 plays important roles in many malignancies including breast cancer. To explore the potential association of EPS15 with the clinical outcome of breast cancer, we conducted gene expression survival analysis using six independent datasets, checked its expression quantitative loci and their associated genes, and explored the networking of these genes with EPS15. Our results show that over-expression of EPS15 is significantly associated with a favorable clinical outcome of breast cancer, especially in tumors harbouring a positive estrogen receptor status. 21 unique SNPs were found to be associated with EPS15 expression. Among the neighboring genes of these SNPs, five (MTUS1, DOCK5, MSRA, SLIT3 and SKAP1) are genetically connected with EPS15 and its physical partners. These genes including EPS15 also show significant concurrent expressions, and four exhibit distinct relevance regarding patient survival. High expressions of EPS15 and MSRA show a distinct combinatorial favorable survival, suggesting the clinical relevance of their co-activation. In summary, over-expression of EPS15 is a potential favorable prognostic marker in breast cancer, which can be used clinically alone or together with other genes such as MSRA to avail therapeutic decision-making.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...