Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals heat stress-induced injury in rat small intestine via activation of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways†
Abstract
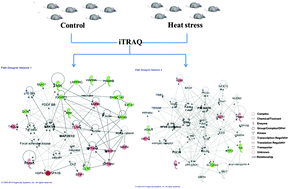
The intestinal epithelium plays a critical role in absorbing nutrients and maintaining the integrity of the gut barrier. Extreme heat stress induces damage to the intestinal epithelium. However, the protein expression changes and the mechanism behind this damage remain poorly understood. In this study, morphological observation showed that heat stress induced desquamation of intestinal epithelial cells, and destruction of intestinal microvilli and mitochondria. Heat stress-induced changes in the intestinal proteome were quantified using the iTRAQ method followed by mass spectrometry and software analysis. A total of 1689 proteins were identified in rat intestine tissue, of which 41 showed significantly altered expression between the heat stressed and control groups. However, these proteins with significant alterations were involved in biological processes such as cellular assembly and organization, developmental disorder, organismal injury and abnormalities, and inflammation. We found that members of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways act as hub proteins in the network interaction analysis. Furthermore, western blot analysis verified that the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways were activated by heat stress as expected. This study suggests that heat stress induces cell cytoskeleton reorganization and an inflammatory response, and the activation of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, which may ultimately contribute to intestinal injury.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...