PerFlexMEA: a thin microporous microelectrode array for in vitro cardiac electrophysiological studies on hetero-cellular bilayers with controlled gap junction communication
Abstract
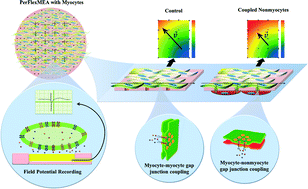
The new microelectrode array device presented is called PerFlexMEA and it enables controlled coupling between myocytes and nonmyocytes used in cardiovascular conduction studies. The device consists of an 8 μm thin parylene microporous membrane with a 4 × 5 microelectrode array patterned on one side. Myocytes and nonmyocytes can be plated on either side of the parylene membrane to create a tissue bilayer. The 3–3.5 μm diameter pores allow inter-layer dye and electrical coupling without transmembrane cell migration. Cell migration was found to vary with cell-type and micropore diameter. Pore density can be varied based on desired coupling ratio. The flexible parylene membrane is packaged between two rigid thermoplastic layers, such that the microelectrode array region is exposed, while the rest of the device remains insulated. The packaged PerFlexMEA fits in a 60 mm culture dish. Recording experiments are performed by simply plugging it into a commercially available multielectrode amplifier system. Recorded signals were processed and analysed using scripts generated in MATLAB. Our experimental results provide evidence of the reliability of this device, as conduction velocity was observed to decrease after inducing lateral hetero-cellular controlled coupling between myocytes and HeLa cells expressing connexin 43.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...